NASA Mars Water Discovery: According to reports dated April 19, 2025, NASA has confirmed the discovery of water on the planet Mars. This water is soon expected to be brought back to Earth as a sample for further research. The discovery has been made possible through various missions, including Lunar Prospector, Mariner 9, Viking Lander, Mars Exploration Rover, Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, Phoenix Lander, Mars Odyssey, and the InSight Lander. These missions have collectively contributed to locating, collecting, and analyzing water samples from Mars. The sample currently being returned to Earth could be instrumental in understanding the potential for life and the planet’s history or future.

When and Where Was It Discovered?
According to sources, water on Mars has not been found in a single location but in various forms across different regions. In addition to water, the discovery included the presence of a carbon dioxide (CO₂) atmosphere, which could offer valuable insights into Mars’ past and its potential to support life. Water has been detected in the form of vapor, subsurface water, and deep-soil moisture. Discoveries have been made across decades, from the 19th to the 21st century. The first significant evidence of water vapor was observed in 1971 by the Mariner 9 mission, while ice patches were more recently found in 2024.

Who Was Behind the NASA Mars Water Discovery?
This discovery was not the work of a single individual but a collective achievement by numerous scientists and engineers working on various NASA missions, including Mariner, Viking, Pathfinder, Mars Global Surveyor, Mars Odyssey, and the Mars Exploration Rovers.

How Did the NASA Mars Water Discovery Happen?
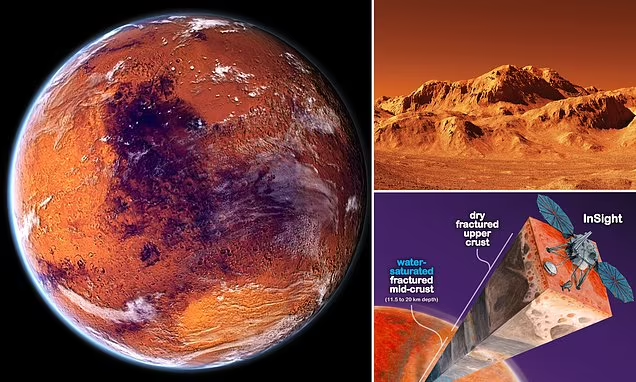
Water on Mars was discovered through decades of exploration and data collection from multiple spacecraft. The Viking missions (1976) observed dry riverbeds, suggesting past liquid water. In 2001, the Mars Odyssey orbiter detected ice beneath the Martian surface, which the Phoenix Lander confirmed in 2008. The Curiosity rover (2012) found evidence of ancient lakes and streambeds. In 2015, dark streaks on Martian slopes hinted at seasonal salty water flows. One of the most groundbreaking discoveries came in 2018, when radar data from the Mars Express orbiter suggested the presence of a lake of liquid water beneath the south polar ice cap.

What Type of Water Was Found on Mars?
The water found on Mars exists primarily in the form of water ice (H₂O ice), which is relatively rare and precious in the Martian environment. Other forms include surface ice, ice patches, glaciers, and water vapor. While liquid water on the surface is currently unlikely due to the planet’s thin atmosphere and extreme temperatures, subsurface water remains a focus of study.

What Are the Challenges of Discovering Water on Mars?
NASA has faced numerous challenges in the search for water on Mars, including:
-
A thin atmosphere.
-
Harsh Martian environmental conditions.
-
Extreme surface temperatures.
What Are the Challenges of Discovering Water on Mars? -
Frequent and intense dust storms.
-
Vast distances between Earth and Mars.
-
Variability in the types and locations of water sources.
Details on the Sample Return and Research.
The Mars Sample Return (MSR) mission is one of the most ambitious scientific projects in planetary exploration. Its goal is to return Martian rocks, soil, and possibly water samples to Earth for advanced analysis—capabilities that current Mars rovers and instruments do not possess. The mission is a joint effort between NASA and the European Space Agency (ESA). It involves the Perseverance Rover and a future lander (still in development), which will collect and transport the samples for return to Earth.

What Is the Future of This Mission?
The return of Martian water samples opens exciting possibilities for future exploration, including:
-
Deeper exploration and preservation of the Martian environment.
-
Potential collaboration between global space agencies.
-
Further proof regarding the potential for past or present life on Mars.
What Is the Future of This Mission? -
Enhanced understanding of Mars’ geology, atmosphere, and evolution.
-
Upgraded technologies and missions for the eventual human exploration of Mars.
-
Strengthened connections between Earth and Mars for future colonization or research bases.
Also Read This: Mere Husband Ki Biwi: Details on the Direction, production, writing, theme, cast, and OTT on April 18 details.